On June 11, the second Belt and Road Conference on Science and Technology Exchange was held in Chengdu. During the conference, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, the 54th Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation, and the Yangtze River Delta Industrial Innovation Center for Quantum Technology signed a cooperation agreement with the University of São Paulo, the Federal University of Campina Grande, and the Federal University of Paraíba in Brazil. The agreement announced a joint initiative to conduct innovative applied research on quantum computing technology in the field of space science.
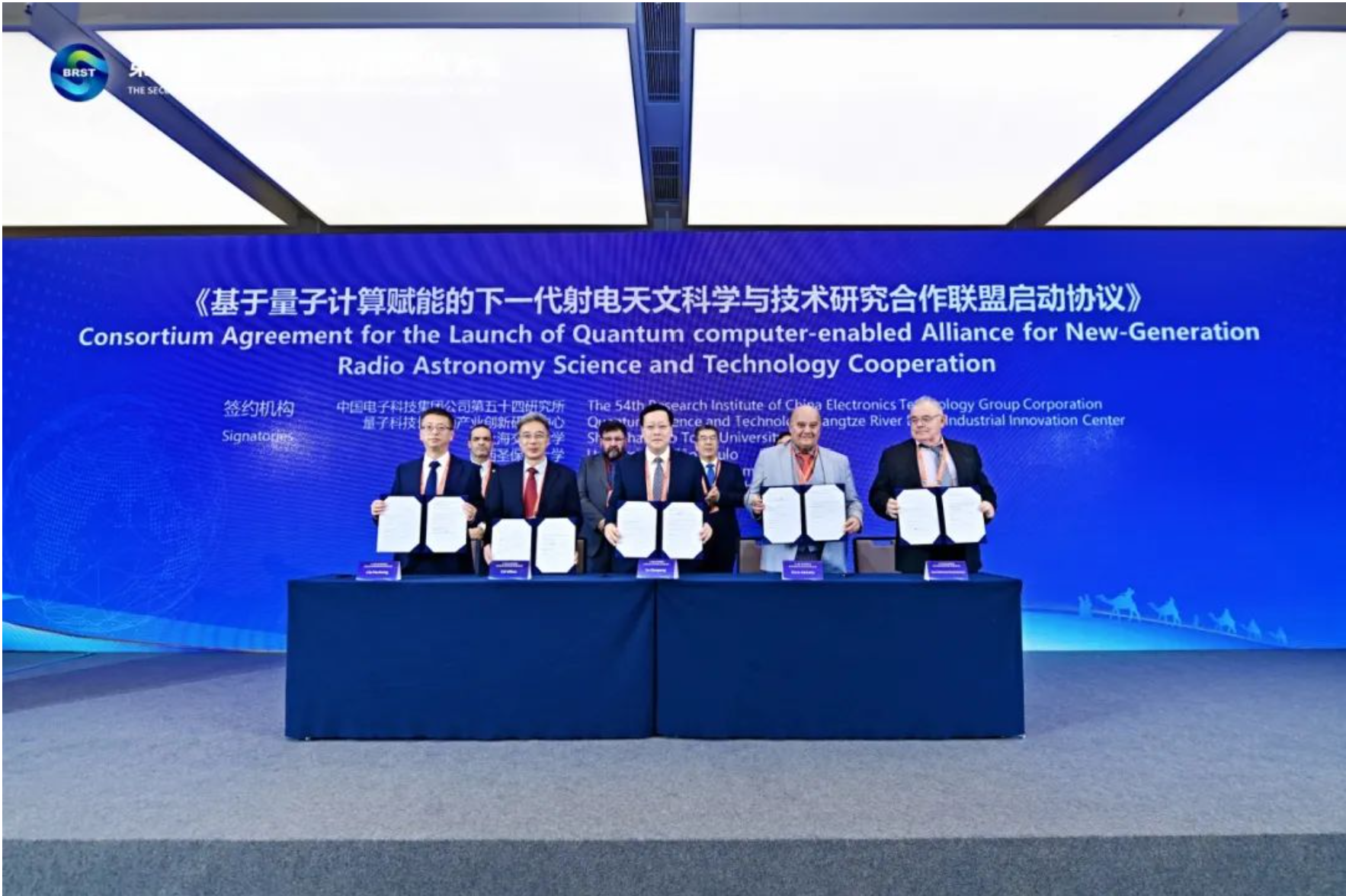

Under the theme "Building an Innovative Silk Road and Promoting Cooperative Development," this year’s conference attracted nearly 2,000 participants from over 80 countries. The China-Brazil Quantum Space Science Cooperation Project emerged as a highlight, reflecting the evolution of the Belt and Road Initiative from infrastructure connectivity to deeper collaboration in scientific and technological innovation.
As a crucial window for exploring the mysteries of the universe, radio astronomy studies fundamental scientific questions such as cosmic evolution and black hole characteristics by detecting radio waves emitted by celestial objects. With the continuous expansion of global radio telescope arrays, the demand for data processing has grown exponentially. Traditional computing methods can no longer meet the real-time processing requirements of massive astronomical data. Quantum computing, leveraging its inherent advantages, is poised to break through bottlenecks in space science research and may become a key technology in addressing these challenges.
According to the agreement, the Chinese and Brazilian sides will focus on cooperation in quantum algorithms for big data processing in radio astronomy, quantum technology-based coordinated control systems for telescope arrays, and the establishment of an international joint laboratory for quantum space science. Shanghai Jiao Tong University, through its School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, will play a pivotal role in this collaboration, leading critical tasks such as the development of big data processing algorithms for space observation science, inversion techniques, and scientific interpretation.
Liu Fucheng, Dean of the School of Aeronautics and Astronautics at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, stated that this cooperation encompasses not only technological research and development but also talent cultivation and exchange mechanisms. The school plans to facilitate annual exchanges of researchers and students to accelerate the progress of the project.
Cai Aihua, Technical Director of the Yangtze River Delta Industrial Innovation Center for Quantum Technology, noted that the integration of quantum computing and radio astronomy could enable faster identification of transient cosmic phenomena such as fast radio bursts and even lead to the discovery of new astrophysical phenomena. Brazilian representative, Academician Elcio Abdalla, emphasized that this collaboration will significantly enhance astronomical observation capabilities in the Southern Hemisphere, particularly in exploring the central region of the Milky Way.



 CH
CH